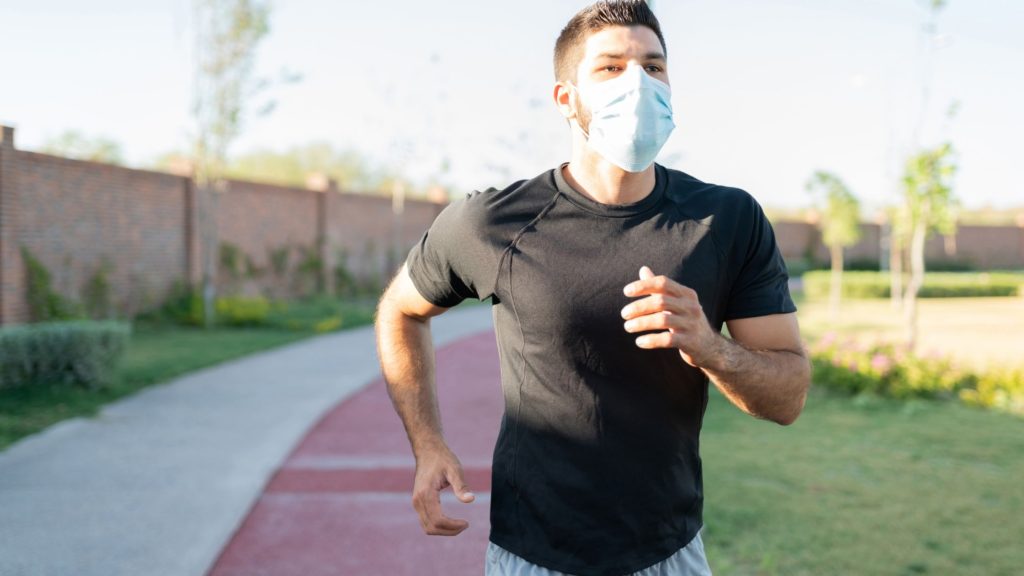
Regular physical activity and exercise can prevent the severity of covid-19 infection find a new study. The study was published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine that links the positive effects of exercise with improved immunity against SARS-CoV-2 infection1. It is already known that physical activity and exercises are important in the prevention of respiratory infections, not only this, it has benefits for the overall health of the musculoskeletal system the joints the bones the muscles and even research has found that regular exercises can help to reduce the chances of lung cancer.
So this study is very crucial in the era of covid-19, it reminds us of how important is to exercise and keep ourselves physically fit for prevention and protection from any kind of chest infection, especially the covid-19 infection. So let’s try to understand more about this research.
Regular exercise linked with reduced risk of COVID-19 infection
We all have witnessed the devastating effects of COVID-19 during the years 2020 and 2021, people getting infected, hospitalised and even death due to oxygen deprivation. It was more devastating for elderly and people with other morbidities. Exercises are known to strengthen the immunity that helps fight chest infection, it also reduces the stress level that indirectly affects the immune system. Inshorts, exercises, including breathing exercises are very beneficial in keeping the respiratory system healthy.
However, for researchers, there was no clear link between physical exercise and reduced effect of covid-19 infection. The current research was published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine for which researchers selected 16 different research papers that were published between November 2019 to July 2020 22. They carefully selected the papers that included participants with more than 18 years of age, their physical activities were measured with observational studies. They cross-checked all these data
Exercise improves immunity against COCID-19 finds result
Research has included 16 studies and they found that regular exercises are associated with fewer chances of getting infected by covid-19. The risk of getting infected by SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19 reduced by over 11%. People with a regular habit of exercise had a lower risk of hospital admission that reduced by 36%, and most importantly had a 43% lower risk of death from COVID-19 in comparison to their less inactive peers.
What does it mean for us?
If you are already into regular physical activity then you need not have to worry. But if you are leading a sedentary lifestyle, get yourself involved in physical activity and exercise to increase immunity against covid-19. The research also says that 500 metabolic equivalents of task (MET) of physical activity per week which is equivalent to 150 min of moderate exercise and 75 min of vigorous exercise per week is important.
Keep Reading: Dummies Guide to Exercising for Diabetes| 12 Easy Workouts to Follow From Today
The author is a physiotherapist who has been practising for the last 17 years. He holds a Bachelor's in Physiotherapy (BPT) from SVNIRTAR (Swami Vivekananda National Institute of Rehabilitation and Research), one of the prestigious physiotherapy schools in India.
Whatever he learns dealing with his patient, he shares it with the world through blogs and e-books. He also owns a YouTube channel, "Sunit Physiotherapist" with over 8 lakh active subscribers. Here, he shares everything he gets to learn serving the patient.