Last updated on June 14th, 2022 at 10:57 pm
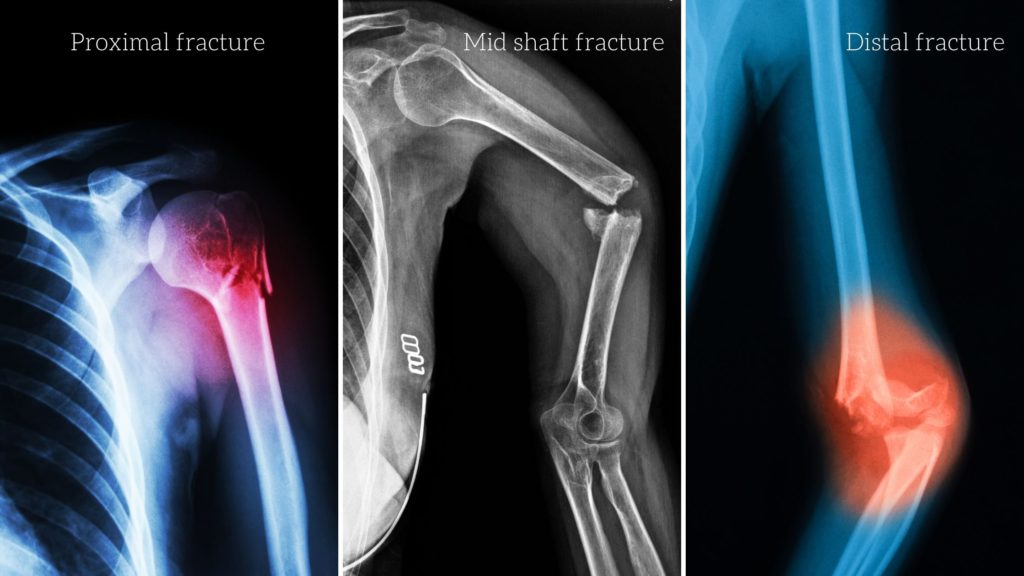
Our upper arm is made of a single thick long humerus bone. Due to some mishap if we break our arm it’s actually a fractured humerus. Fracture can happen at upper end of humerus, middle part or at the lower end of the bone. Depending on the site of fracture this could be classified into three different types. In this article, we will discuss all the three different fracture humerus classification, their sub type and their potential causes.
Fracture humerus classification simplified
Depending on the nature and force of impact the
Let me share a true incidence to make it more clear, there was a middle-aged male patient who suffered such a fracture and he described his story as something like this.
“One fine morning I was on the regular morning walk. I was enjoying my walk when suddenly I stumbled upon a rock by the side of the road and fell down. I outstretched my hand to fall on my hand only to find that my hand was in great pain. My doctor told me that I have broken my arm bone and it needs to be fixed by immobilising it using a sling or POP cast”.
When we fall we have a tendency of falling with hands outstretched. Outstretching of the hand is an involuntary reflex action which protects us from injuring our head and the body. But sometimes it results in the injury of the hand and may cause fractures arm, forearm and hand.
The most common cause fracture is falling on the outstretched hand. Falling in an outstretched hand is actually a preventive reflex to prevent ourselves from hurting. It can be during waking while running or simply you fell from the bike.
#1 Proximal humerus fracture
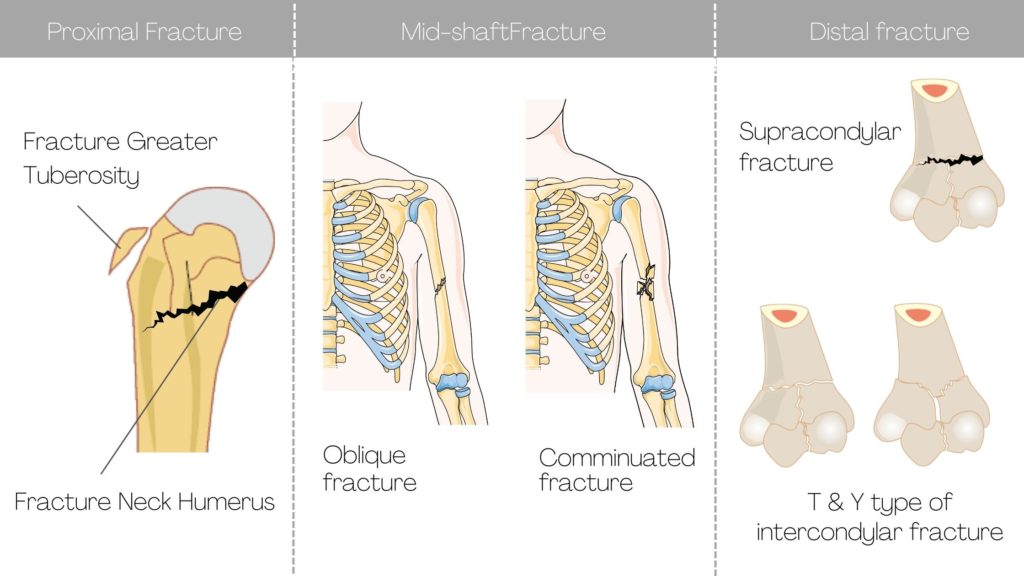
In proximal humerus fracture, the fracture occurs on the upper end around the head and neck of the humerus bone. The most common site of fracture is the fracture at the neck of the humerus and the Fracture Greater Tuberosity. The fracture could be displaced or un-displaced depending on the impact of the injury.
The Proximal humerus fracture is further classified into four segments based on the number of fracture displaced segments or parts. This popular classification was proposed by Neer (1).
Neer Classification for proximal humerus fracture
| Type | Description | |
| 1 | One-Part Fractures | No fragments meet the criteria for displacement; a fracture with no fragments considered displaced is defined as a one-part fracture regardless of the actual number of fracture lines or their location. |
| 2 | Two-Part Fractures | One segment is displaced, which may be the greater tuberosity, lesser tuberosity, or articular segment at the level of the anatomic neck or surgical neck. |
| 3 | Three-Part Fractures | With a three-part fracture, one tuberosity is displaced and the surgical neck fracture is displaced. The remaining tuberosity is attached, which produces a rotational deformity. |
| 4 | Four-Part Fractures | All four segments (both tuberosities, the articular surface, and the shaft) meet criteria for displacement. The articular segment typically is laterally displaced and out of contact with the glenoid. This is a severe injury and carries a high risk of avascular necrosis. |
#2 Fracture mid-shaft humerus
As the name suggests, fracture mid-shaft of humerus is a fracture at the middle portion of the shaft of the humerus bone. This fracture is also commonly seen in adult people of any age. It is of three types and again the type depends on the nature and type of fracture force. Broadly it is categorised under three types.
- Spiral fracture: When a rotational or twisting force assaults the arm the resulting fracture takes in a spiral manner. This is why it is named the spiral fracture.
- Oblique or transverse fracture: when force is angular in nature it leads to a fracture which runs obliquely in the shaft of the humerus.
- Communiated fracture: The fractured part gets fragmented into several pieces. This may result due to a direct blow or direct assault or attack on the arm bone.
#3 Proximal humerus fracture
It is the fracture at the lower end of the humerus bone. Depending on the site of the fracture, it could be intercondylar fracture, Supracondylar fracture humerus. Inter-condylar fracture is also very common in adults but also largely reported in the young person. It happens due to a direct fall on the tip of the elbow. The fracture can be two-part or a comminuted fracture. The treatment depends on whether the fracture is displaced or undisplaced.
Fracture on the lower end of the humerus around the elbow can lead to an increase or decrease in carrying angle of elbow.
Final word
Treatment of the fracture of arm bone depends on the type of fracture. Details on each and every type of fracture are beyond the scope of this discussion.
Journal reference:
- Carofino, B. C., & Leopold, S. S. (2013). Classifications in brief: the Neer classification for proximal humerus fractures. Clinical orthopaedics and related research, 471(1), 39–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-012-2454-9
The author is a physiotherapist who has been practising for the last 17 years. He holds a Bachelor's in Physiotherapy (BPT) from SVNIRTAR (Swami Vivekananda National Institute of Rehabilitation and Research), one of the prestigious physiotherapy schools in India.
Whatever he learns dealing with his patient, he shares it with the world through blogs and e-books. He also owns a YouTube channel, "Sunit Physiotherapist" with over 8 lakh active subscribers. Here, he shares everything he gets to learn serving the patient.





Pingback: 9 Easy shaft of humerus fracture exercises & physiotherapy management - Physiosunit
Pingback: Shaft of humerus fracture: Treatment & physiotherapy. : Physiosunit