Last updated on June 16th, 2025 at 05:55 pm
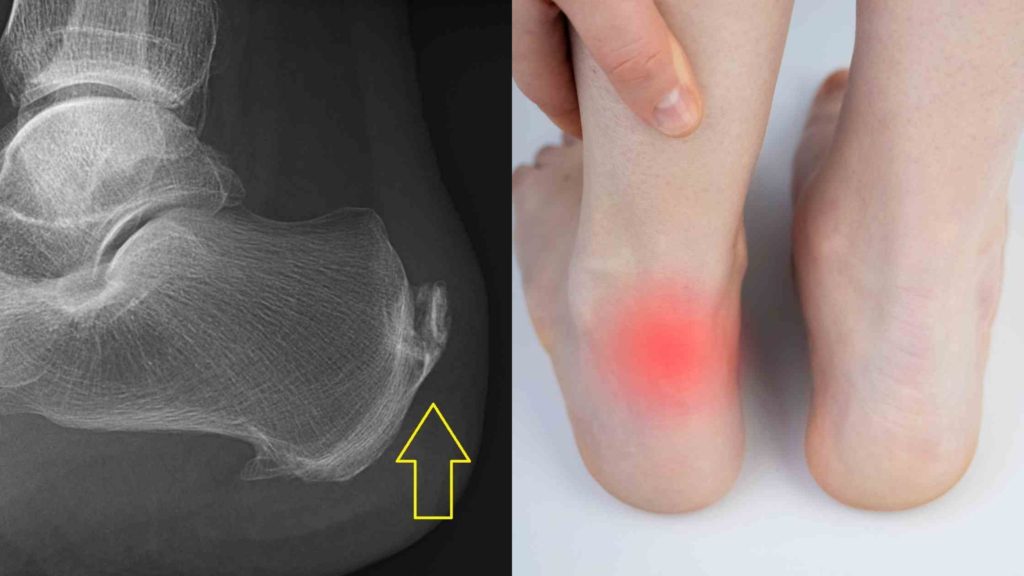
- Calcification in Achilles Tendon is a condition that causes the hardening of the Achilles tendon due to calcium buildup.
- This condition can cause pain, stiffness, and limited ankle joint movement.
- Exercise can help improve the Achilles tendon’s strength, flexibility, and overall health, reducing calcification symptoms.
- Working with a healthcare professional to design a safe and effective exercise program that meets your individual needs is important.
- The exercises may include stretching, strengthening, range of motion exercises, and low-impact activities such as swimming or cycling.
Pain and swelling just behind the ankle joint could be due to calcification in the Achilles tendon. The Achilles tendon can be calcified due to various factors, including injury, ageing, or a medical condition.
The sufferer of this kind of pain usually complains of pain at this particular point and difficulty in walking or stair climbing. In addition to exercises for Achilles tendonitis, physiotherapy treatment is also essential.
In this blog post, we’ll explore calcification in the Achilles tendon, its causes, symptoms, and exercise treatment options.
- What Is Calcification in the Achilles Tendon?
- Achilles Tendon Calcification: Causes & Risk Factors
- Symptoms of a Calcified Achilles Tendon
- Physiotherapy Treatment for Achilles Tendon Calcification
- Best Exercises for Achilles Tendon Calcification
- Footwear & Lifestyle Modifications for Relief
- When Is Surgery Needed for Achilles Tendon Calcification?
- FAQs About Achilles Tendon Calcification
What Is Calcification in the Achilles Tendon?
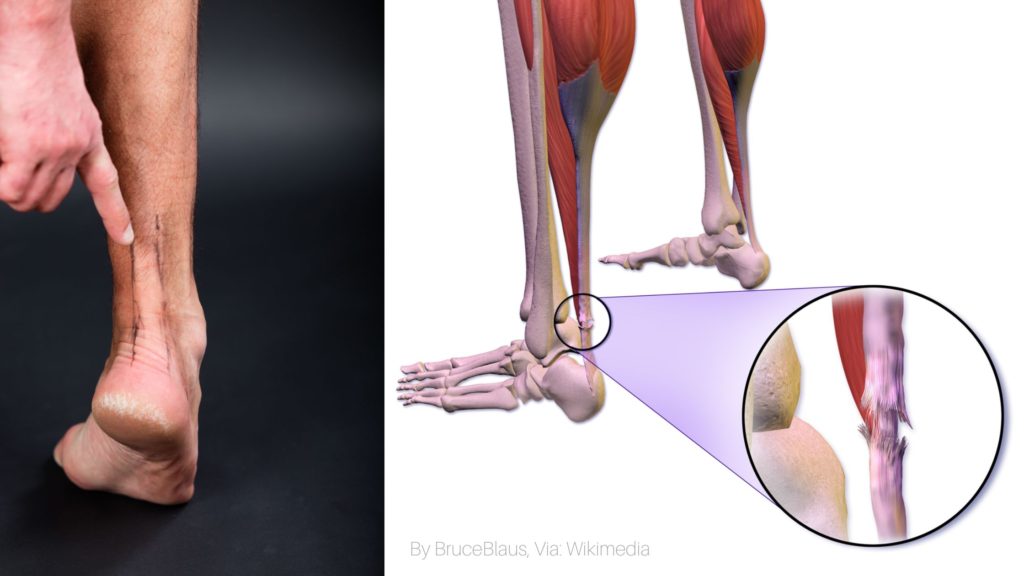
Calcification of the Achilles tendon occurs when there is an abnormal deposition of calcium, leading to the formation of extra bone where the tendon inserts into the heel bone. In some cases, it can extend into the main body of the tendon, causing calcific tendinopathy of the main body2.
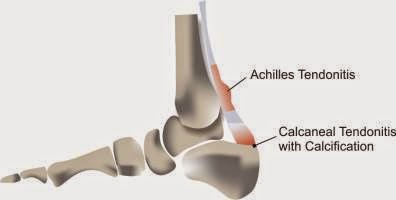
Though there could be other causes of pain at the back of the heel, like calcaneal bursitis and Haglund’s deformity, the common cause is retrocalcaneal tendinitis with calcification.
Achilles Tendon Calcification: Causes & Risk Factors
The exact cause is unknown, but if the Achilles tendon insertion is continuously subjected to stress and stretch for days and months, it results in irritation at his point. This slowly, with time, develops swelling and calcification, leading to a calcified Achilles tendon.
Previous research also revealed that, as a person ages, the likelihood of developing ICT rises, especially for those who have diabetes mellitus and hypothyroidism1.
There could be one of the two factors, intrinsic cause or extrinsic cause, or both factors simultaneously working to give irritating stress at an insertional point on the back of the calcaneum.
Intrinsic Causes of Achilles Tendon Calcification
Some of the intrinsic factors that can lead to calcification of the Achilles tendon include old internal injuries, tightness or contracture of the muscle or tendon, and deformity in the muscle or tendon.
Old internal injuries can cause calcium deposits to accumulate in the tendon over time.
Tightness or contracture of the muscle or tendon can cause stress on the tendon, which can lead to calcification. Deformity in the muscle or tendon can also cause stress on the tendon, leading to calcification.
- Tendo Achilles tightness.
- Hamstring tightness
- Flat foot: In flat foot, the arch of the foot becomes flat. Because of this, the heel bone is tilted lower than normal while the back of the heel is tilted a bit higher.
This may force the posterior-superior portion of the heel into the Retrocalcaneal Bursa and Achilles Tendon.
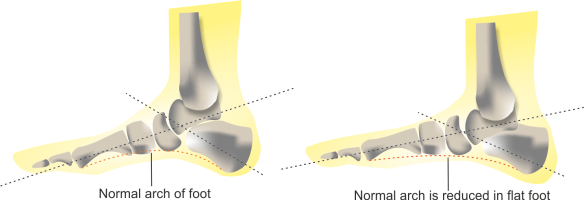
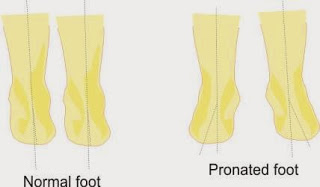
4. Pronated foot: A pronated foot is a type of foot deformity where the arch of the foot collapses and the foot rolls inward. This can cause pain, discomfort, and problems with balance and stability.
People with pronated feet may benefit from special shoes or orthotics to provide support and correct their foot position.
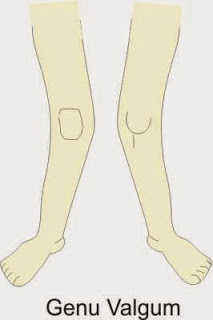
5. Genu valgum: Genu valgum, also known as knock knees, is a common knee deformity where the knees angle inward and touch each other when the legs are straightened.
This may be due to various reasons, such as a developmental problem in childhood, injury, or a genetic condition.
The condition may cause prolonged pain, discomfort, and difficulty walking, running, or standing. Treatment options may vary depending on the severity of the condition and may include physical therapy, braces, or, in severe cases, surgery.
Extrinsic Factors Leading to Calcification
Extrinsic factors that can cause calcification of the Achilles tendon include overuse of the tendon, improper footwear, and poor training techniques.
Overuse of the tendon can cause repetitive stress on the tendon, leading to inflammation and eventual calcification.
Improper footwear can also cause stress on the tendon, leading to calcification. Poor training techniques can cause improper alignment of the body, leading to stress on the Achilles tendon and eventual calcification.
- Activities that involve excessive jumping and running.
- Dancing
- Cycling
- Trauma/ injury
- Gastrosoleous muscle weakness/inefficiency.
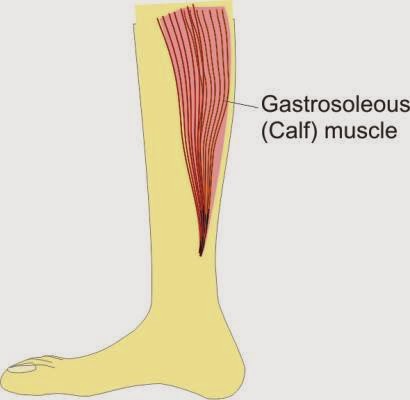
Symptoms of a Calcified Achilles Tendon
A calcified Achilles tendon is a condition where calcium builds up in the tendon, causing it to harden and become less flexible. This can lead to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in the affected leg.
Symptoms of a calcified Achilles tendon may include aching or sharp pain in the back of the heel or ankle, difficulty walking or running, and tenderness or swelling in the area.
- Pain during running, prolonged jumping.
- Strenuous activity/athletic activity on hilly surfaces.
- Inability to participate in athletic activities.
- As it progresses, one complains of pain & stiffness, resolving with movement and activities.
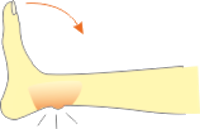
- Restriction of Dorsi Flexion of Ankle
- Localised nodule/ swelling.
- Strong resisted plantar flexion is painful.
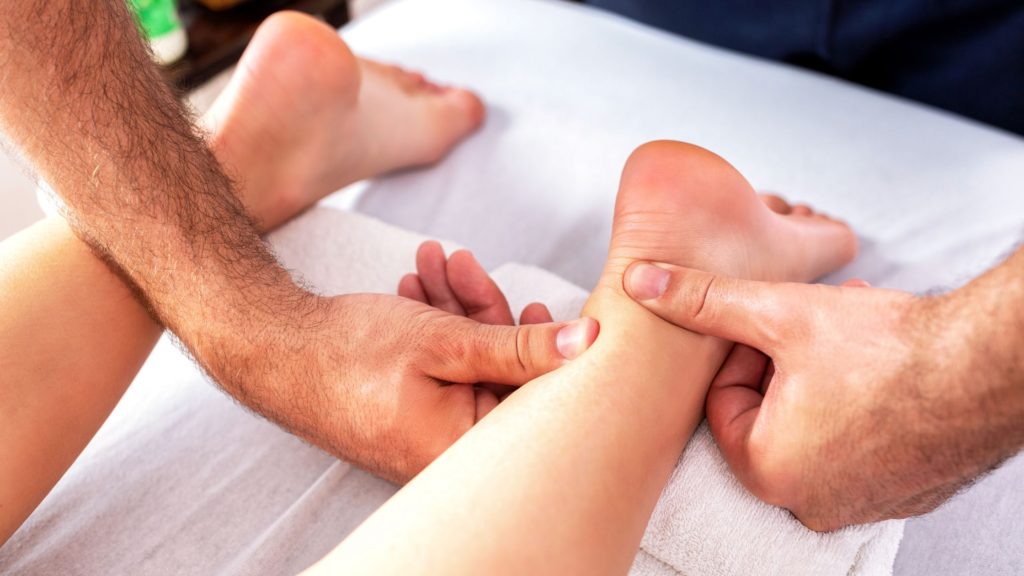
Physiotherapy Treatment for Achilles Tendon Calcification
During physiotherapy treatment, a physical therapist will use various techniques to help reduce inflammation and improve range of motion. This may include manual therapy, such as massage and stretching, as well as exercises to strengthen the muscles in the affected area.
In addition to these techniques, a physical therapist may also recommend using orthotics or other supportive devices to help alleviate pressure on the Achilles tendon.
They may also advise on lifestyle changes, such as modifying footwear or adjusting exercise routines, to help prevent further injury.
Physiotherapy aims to prevent further damage, resolve inflammation, and prevent reoccurrence. Physiotherapy treatment can be categorised into the acute phase and the chronic phase.
Acute Phase: Rest, Ice & Inflammation Control
- Rest
- Avoid precipitating activities like running and jumping.
- Cryotherapy/ ice therapy
Chronic Phase: Stretching & Strengthening Exercises
- DTFM (Deep Transverse friction Massage)- done to smoothen the nodule.
- Stretching of tendo Achilles done.
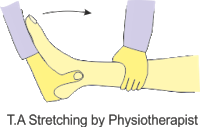
- Ultrasonic therapy.
- Ice therapy.
- Strengthening exercise

Achilles Heel Guard: comfortably protects the back of the heel and the lower portion of the Achilles tendon from shoe pressure and friction.
Best Exercises for Achilles Tendon Calcification
Research suggests that an eccentric heavy load is beneficial in curing this tendinopathy. We recommend slowly progressing from light stretching exercises to heavy-load exercises3.
We have a dedicated article on this topic. We recommend referring to “Easy Achilles tendonitis stretches and other exercises for Pain Relief” for a comprehensive guide.
Footwear & Lifestyle Modifications for Relief
In addition to physiotherapy and exercises, modifying footwear is essential for a long-term effect. Here are a few modifications backed by studies:
- Using heel lifts: According to study, using heel lifts not only improved pain severity after 2 weeks but also immediately reduced pain during walking. It also improved the walking pattern and speed4.
- Proper shoe fit is also essential. Shoes that are too tight or too loose can exacerbate the condition and cause additional discomfort.
- Choose shoes with good base of support: It’s important to choose shoes that provide ample support and cushioning while also allowing for proper foot and ankle movement.
- If the calcification is severe, a podiatrist may recommend custom orthotics to be worn on the shoes. These specially designed inserts provide additional support and cushioning to the foot5.
- FlAT FEET: Medical grade Orthotic Inserts For common foot pain, arch pain, heel pain, ankle Pain,plantar fasciitis and o…
- 3CM ARCH SUPPORT: Rigid arch support distributes and minimize pressure in the foot .DEEP HEEL CRADLE keep the foot bone …
- ALL DAY COMFORT MATERIAL :Durable EVA foam base and multi-layer cushion provide long-lasting support and comfort while w…

- HEEL PAIN RELIEF: The heel lift inserts are great For Leg Length Discrepancies, Heel spurs, Heel Pain, Sports Injuries, …
- ADJUSTABLE DESIGN: Adjustable layers allow you to build up the height by adding layers yourself; Strong self-adhesive th…
- HIGH-QUALITY MATERIAL: The heel lift inserts are made of soft and durable medical-grade PU gel. And the fabric is breath…

When Is Surgery Needed for Achilles Tendon Calcification?
Surgery for Achilles tendon calcification is considered a last choice when conservative treatments fail. According to clinical studies, only 5–10% of patients require surgical intervention, typically after 6–12 months of unsuccessful physiotherapy, rest, and medication (Maffulli et al., 2008).
Indications for Surgery
- Persistent Pain & Disability
- Pain that limits daily activities (e.g., walking, stair climbing) despite 6+ months of:
- Eccentric exercises.
- Ultrasonic therapy
- Orthotic modifications
- Pain that limits daily activities (e.g., walking, stair climbing) despite 6+ months of:
- Large Calcium Deposits (>1.5 cm)
- Visible on imaging (X-ray/USG) and causing mechanical obstruction.
- Tendon Rupture Risk
- Advanced calcification weakens the tendon, increasing tear risk.
Surgical Options
- Open Debridement: Removal of calcium deposits + damaged tissue.
- Tendon Reattachment: Needed if >50% tendon is detached during debridement.
Keep Reading: How to Contrast Bath Therapy for Hand & Foot Swelling
Need help with Achilles tendon pain? Book a physiotherapy session or leave a comment below!
FAQs About Achilles Tendon Calcification
The author is a physiotherapist who has been practising for the last 17 years. He holds a Bachelor's in Physiotherapy (BPT) from SVNIRTAR (Swami Vivekananda National Institute of Rehabilitation and Research), one of the prestigious physiotherapy schools in India.
Whatever he learns dealing with his patient, he shares it with the world through blogs and e-books. He also owns a YouTube channel, "Sunit Physiotherapist" with over 8 lakh active subscribers. Here, he shares everything he gets to learn serving the patient.




Pingback: Achilles Rupture Tendon: Everything you should know - Physiosunit
Pingback: How to cure plantar fasciitis in one week - Physiosunit
Pingback: How to cure plantar fasciitisin one week : Physiosunit
What would be best treatment for inflammation with calcification of achilles tendon at the point where achilles tendon insert to calcaneal bone. Currently On Anti-inflammatory tabs.
🙂
Thanx
Heel spurs are often misunderstood sources of heel pain. There are several types and locations of bone spurs in the heel. The spur most commonly assumed to cause pain actually does not, while another spur often unnoticed can create a great deal of pain. This article will discuss these spurs, and their contribution to foot pain.If you want Shoes For Achilles Tendonitis you can get lots of benefit for your foot pain.
Great post