Last updated on May 20th, 2025 at 05:31 pm
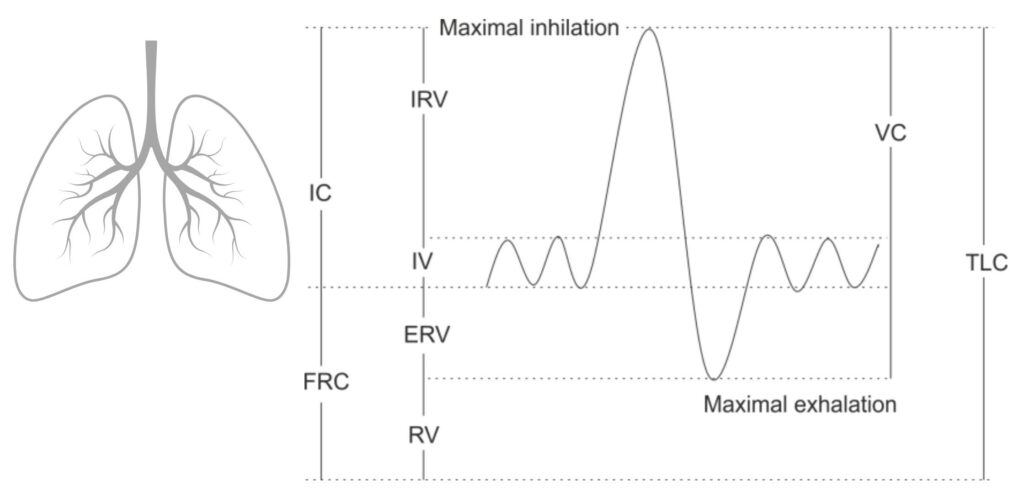
Lung volume and capacity are important metrics for differentiating a normal lung from a diseased one. But, we often get confused between lung volume and lung capacities.
If you are the one who gets all volume and capacities mixed up, this article will help you clear the concept. In this article we will discuss the following:
- The normal range of volume and capacities.
- Lung volume and capacities in obstructive pulmonary disease.
- Lung volume and capacities in restrictive pulmonary disease.
- How actually lung volume is a part of lung capacities.
By the end of this article, you will be somewhat better than you were before.
Lung volume and capacity
Lung volume and capacities measure the amount of air in the lungs when we breathe normally and forcefully. During respiration, air moves in and out of the pulmonary system.
When respiration is normal, less air moves in and out, which increases when our rate of respiration increases during running, etc.
So, lung volume is the measure of the volume of gas/air that moves in and out during
Lung volume explained
Lung volume is the volume of gas that moves in and out during our inspiration and expiration. It is measured in Litres. So, let us discuss how inspiration and expiration are measured in their different forms.
Four lung volumes are:
- Tidal volume.
- Inspiratory reserve volume.
- Expiratory reserve volume.
- Residual volume.
#1 Tidal volume (TV): To understand tidal volume, just sit relaxed on a chair and close your eyes. Now, try to feel your inspiration and expiration (air expelled) with closed eyes.
The volume of air inhaled or exhaled during this rest breathing is the tidal volume. So, tidal volume is defined as “The volume of gas inhaled or exhaled during the resting breath is called the tidal volume”.
#2 Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV): Inspiratory reserve volume is the maximum volume of air that can be inhaled during a forceful inspiration. Actually, it is the additional air to the tidal volume that can be inspired during the forceful inspiration.
To understand it, again sit relaxed on a chair with your eyes closed. Now, take a deep breath to your maximum capacity and expel it out. This, additional air you inhale in addition to the tidal volume mentioned above, is the IRV.
#3 Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV): Expiratory Reserve Volume is defined as the amount of air that can be expelled during forceful expiration.
Now, close your eyes and after taking normal inspiration, try to exhale the maximum amount of air possible. This extra amount of air in addition to normal expiration is ERV.
#4 Residual Volume (RV): Even after forceful expiration, there is some volume of air still left inside the lung. That is, the lung doesn’t get fully emptied even after forceful expiration.
The amount of air that remains in the lungs after maximum exhalation is the residual volume.
So, it can be defined as the volume of air remaining in the lung after ERV has been done.
Lung capacities explained
The four lung capacities are:
- Inspiratory capacity.
- Vital capacity.
- Functional residual capacity.
- Total lung capacity.
#1 Inspiratory capacity (IC): Inspiratory capacity is the volume of air that can be inspired from the end of the tidal expiration or the volume of air that can be inspired forcibly after a normal inspiration.
So, it is the sum of Tidal Volume (TV) + Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV).
#2 Vital Capacity (VC): Vital Capacity (VC) is defined as a change in volume of the lung after maximal inspiration followed by maximal expiration is called Vital Capacity of lungs.
It is the sum of tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume and expiratory reserve volume. The vital capacity of normal adults ranges between 3 to 5 litres.
It is the total volume of air within the lung that is under volitional control. It is the sum of IRV + TV + ERV.
VC is actually Forced Vital Capacity. To measure it, first, achieve maximum inspiration then forcibly expel all the air as fast as possible into a measuring device.
#3 Functional residual capacity (FRC): It is the volume of air that remains after the tidal expiration. So, it is the combination of RV + ERV.
#4 Total Lung Capacity (TLC): It is the total volume of air that remains in the lungs/thorax after maximum inspiration.
It is the sum of IRV + TV + ERV.
Lung volume and capacity graph
We can represent all these four lung volumes and four capacities in a graph. Once again carefully read the descriptions on volume and capacities and then try to interpret it through this graph.
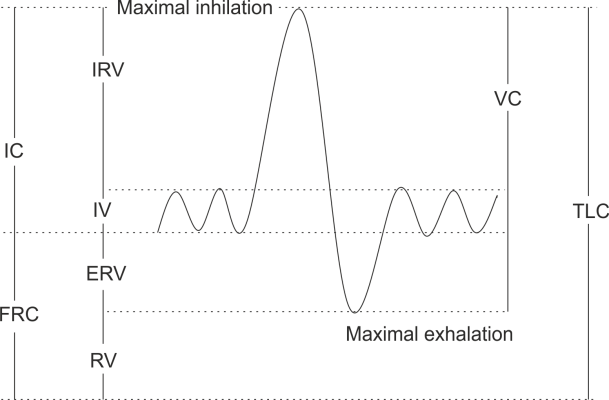
Normal lung volumes and capacities chart
| VOLUME | CAPACITY | ||
| TV | 500 | IC | 3000 |
| IRV | 2500 | VC | 4000 |
| ERV | 1000 | FRC | 2500 |
| RV | 1500 | TLC | 5500 |
| All numbers in: ml (mili leter) |
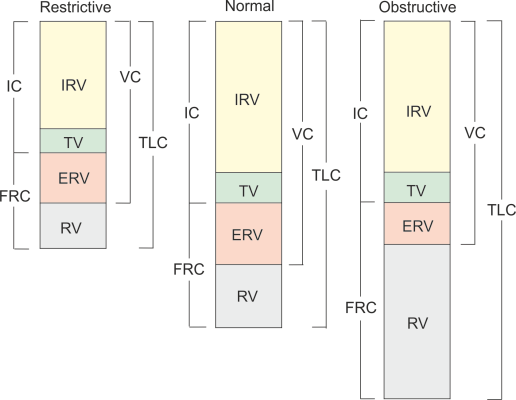
The difference between obstructive and restrictive pulmonary disease
Obstructive and Restrictive pulmonary disease shows different lung volumes and capacities. In restrictive pulmonary disease, all the capacities of the lung are reduced and in obstructive pulmonary disease it all increases.
Let us try to understand it through this graph.
Factors affecting lung volume and capacities
There are many factors that affect static lung volumes/capacities. The factors like age, gender, weight, height and ethnicity are the main physiological determinants of static lung volumes/capacities.
However, there are other factors which should be considered. Like, level of physical activity, regular exercise, especially swimming and endurance training.
Alternatively, ascending to a high altitude may decrease lung volumes, probably due to increased pulmonary blood flow, pulmonary oedema or premature small airway closure 1.
Let’s try to find out how age affects lung volume and capacities.
Effect of age on lung volume/capacities
The respiratory system undergoes various anatomical, physiological and immunological changes with age. The structural changes include chest wall and thoracic spine deformities, which impair the total respiratory system compliance, leading to increased work of breathing.
Respiratory muscle strength decreases with age and can impair effective cough, which is important for airway clearance 2.
All these factors affect the lung volume and capacities, this is why we recommend breathing exercises, which are important for the health of the respiratory system.
If the excess sputum is collected inside the lungs, it also affects breathing, We can get rid of this naturally by following the postural drainage position technique at home.
The lung matures by age 20–25 years, and thereafter, ageing is associated with progressive decline in lung function. The alveolar dead space increases with age, affecting arterial oxygen without impairing carbon dioxide elimination.
The airway receptors undergo functional changes with age and are less likely to respond to drugs used in younger counterparts to treat the same disorders.
Older adults have decreased sensation of dyspnea and diminished ventilatory response to hypoxia and hypercapnia, making them more vulnerable to ventilatory failure during high-demand states (ie, heart failure, pneumonia, etc) and possible poor outcomes 2.
Final word
There are a number of factors that
Further reading: What is Bucket Handle Movement of Ribs, it’s Anatomy
The author is a physiotherapist who has been practising for the last 17 years. He holds a Bachelor's in Physiotherapy (BPT) from SVNIRTAR (Swami Vivekananda National Institute of Rehabilitation and Research), one of the prestigious physiotherapy schools in India.
Whatever he learns dealing with his patient, he shares it with the world through blogs and e-books. He also owns a YouTube channel, "Sunit Physiotherapist" with over 8 lakh active subscribers. Here, he shares everything he gets to learn serving the patient.
Pingback: What is Bucket Handle Movement of Ribs, it's Anatomy - Physiosunit