Last updated on February 27th, 2024 at 05:41 pm

New research has revealed that intake of sufficient dietary nitrate supplementation can improve the function of the diaphragm, thereby improving breathing and coughing. This research is essential for elderly people suffering from breathing problems. This US-based study was published in The Journal of Physiology. The research on mice reveals that dietary nitrate supplementation increases diaphragm peak power in old mice1.
What is the diaphragm, how does its improved function affect breathing, and what are the sources of dietary nitrate? Let’s try to answer all these questions in this article.
Nitrate supplement and improved breathing
The research team at the University of Florida conducted a study on mice and found that dietary nitrate supplementation elicited a pronounced increase in the diaphragm’s contractile function (power).
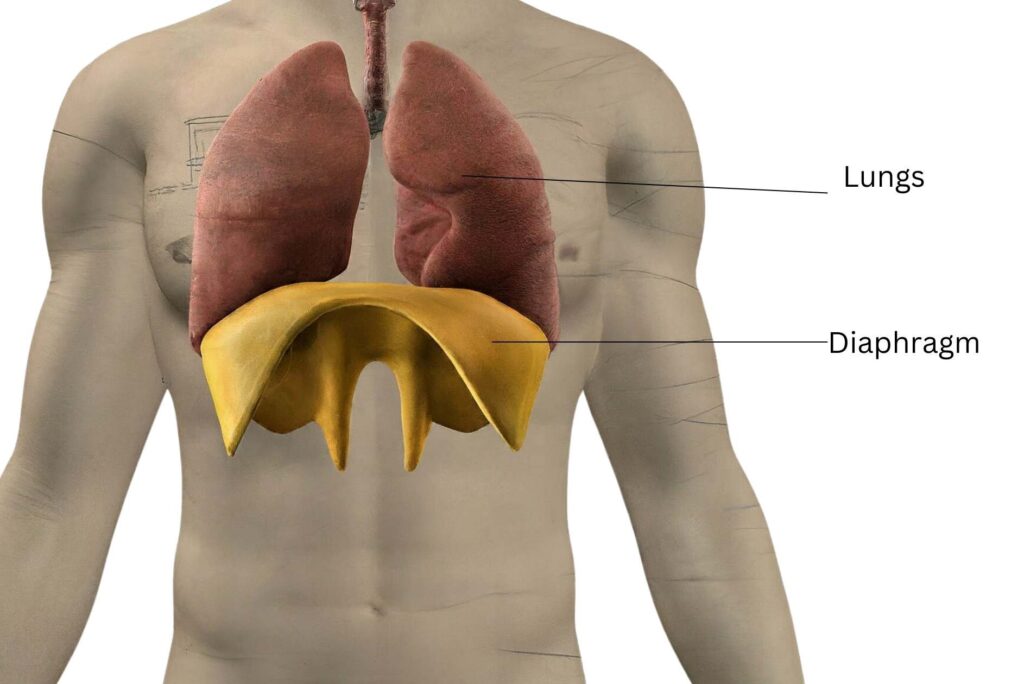
If you are unaware of the diaphragm, it is a vital respiration organ at the base of our thoracic cage. When we inspire, the diaphragm descends to create a vacuum inside the rib cage, and air rushes inside through the nose or mouth. The exact opposite happens when we expire; the diaphragm ascends to push impure air out of the lungs.
However, the function of the diaphragm declines with age, contributing to ventilatory dysfunction, impaired airway clearance, and overall decreased quality of life. Diaphragm isotonic and isometric contractile properties are reduced with ageing, including maximal specific force, shortening velocity and peak power.
Scientists already knew the effect of dietary supplements on the contractile properties of limb muscles in both humans and rodents. However, they were curious about its beneficial effect on respiratory muscles.
But what made researchers conclude that it can also benefit the respiratory muscles?
Research Overview
Researchers hypothesized that dietary nitrate supplementation would improve diaphragm contractile properties in aged mice. To test this hypothesis, scientists performed tests on mice.
They allocated 1 mm of NaNO3 in the drinking water of old (24 months) mice for the next 14 days. After 14 days, they measured the diaphragm function of those mice.
Result
The maximal rate of isometric force development and peak power (40%) increased with nitrate supplementation. In general, the study demonstrates improved diaphragm contractile function with dietary nitrate supplementation and supports using this strategy to enhance inspiratory function in ageing populations.
Dietary sources of nitrate
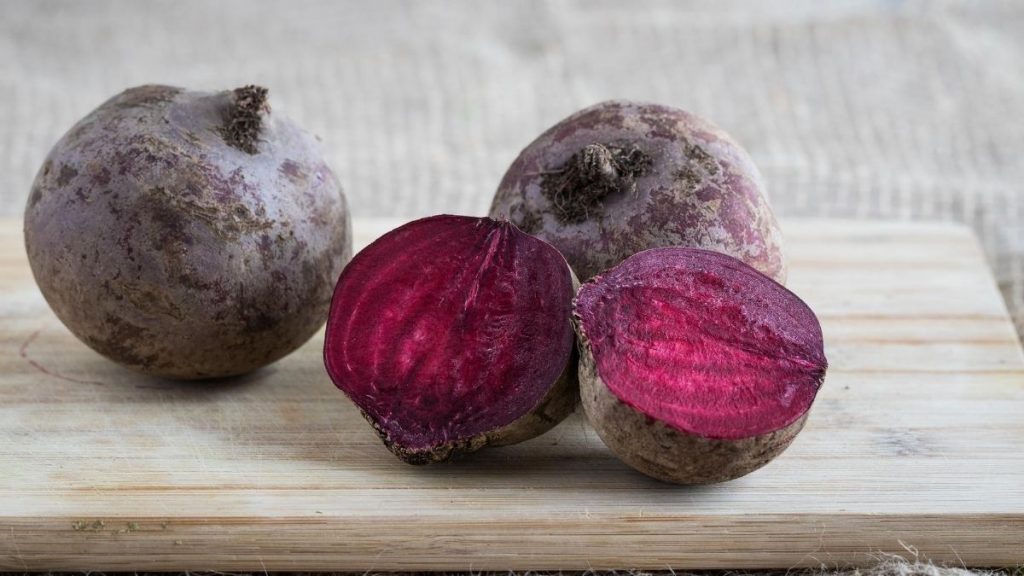

Approximately 80% of dietary nitrates are derived from vegetable consumption; sources of nitrites include vegetables, fruit, and processed meats. These are the rich sources of nitric oxide:
- Beets
- Pomegranate
- Watermelon
- Garlic
- Citrus fruit
- Dark chocolate
Other benefits of dietary nitrates
- In the body, nitrates can turn into nitric oxide (NO) that causes blood vessels to dilate and reduces blood pressure.
- Studies suggest dietary nitrates and nitrites enhance physical performance, especially during high-intensity endurance exercise.
Keep Reading: How to Boost Immune System to Fight Virus
The author is a physiotherapist who has been practising for the last 17 years. He holds a Bachelor's in Physiotherapy (BPT) from SVNIRTAR (Swami Vivekananda National Institute of Rehabilitation and Research), one of the prestigious physiotherapy schools in India.
Whatever he learns dealing with his patient, he shares it with the world through blogs and e-books. He also owns a YouTube channel, "Sunit Physiotherapist" with over 8 lakh active subscribers. Here, he shares everything he gets to learn serving the patient.